1. Map
集合框架类图
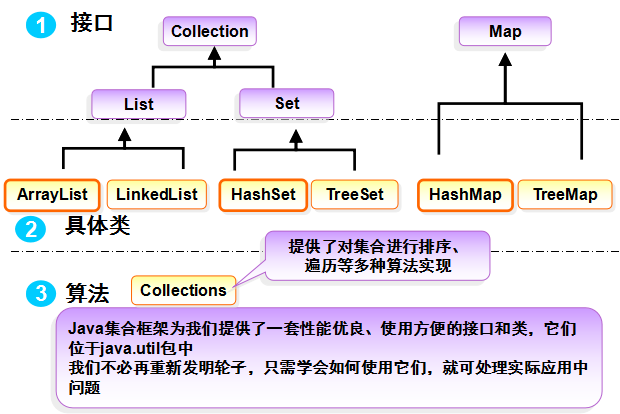
HashMap
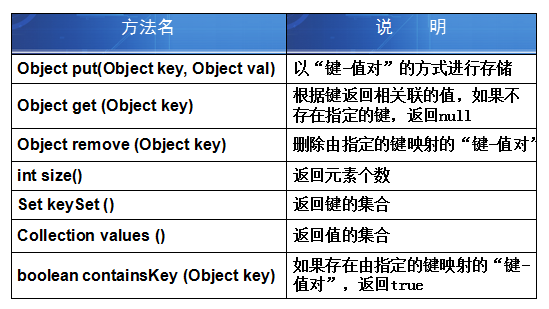
常用方法
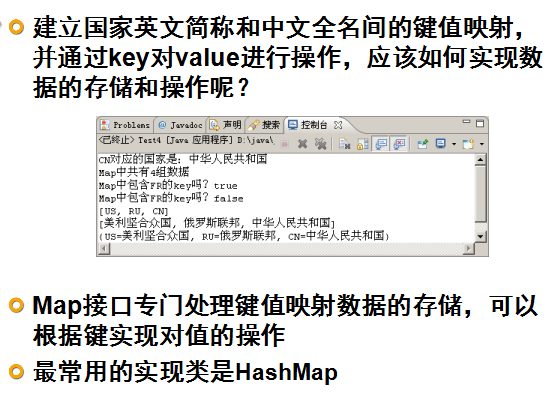
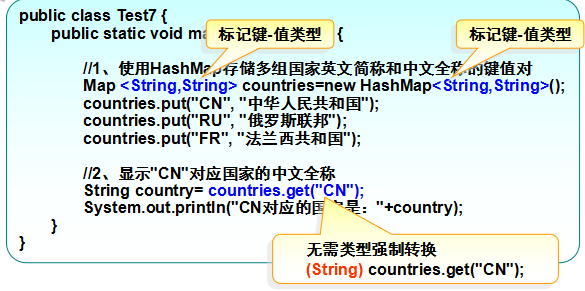
键值对(“key = value”),顾名思义,每一个键会对应一个值。
API
API 是用于构建应用程序软件的一组子程序定义,协议和工具。一般来说,这是一套明确定义的各种软件组件之间的通信方法。
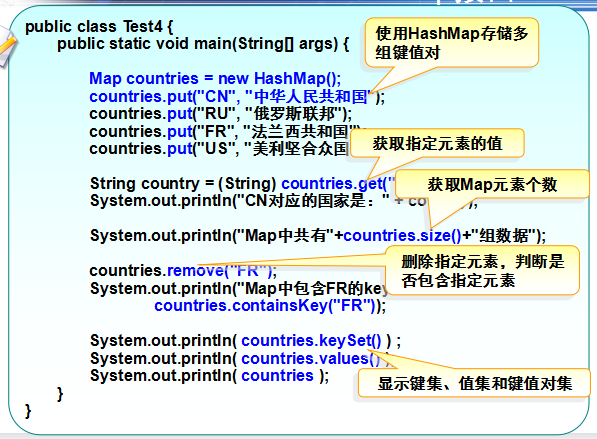
例1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Ex01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map =new HashMap();
map.put(1,"张三丰");
map.put(2,"周芷若");
map.put(3,"汪峰");
map.put(4,"灭绝师太");
map.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println("key:"+k+",value:"+v));
map.put(5,"李晓红");
map.remove(1);
map.replace(2,"周琳");
System.out.println("==============================");
map.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println("key:"+k+",value:"+v));
}
}
|
java8 参考循环输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Map map = new HashMap() ;
map.put(1,"张三1") ;
map.put(2,"张三2") ;
map.put(3,"张三3") ;
map.forEach((k,v)-> System.out.println("序号:"+k+",姓名:"+v));
|
例2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Ex02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] proAy = {"黑龙江省","浙江省","江西省","广东省","福建省"} ;
String[] cityAy = {"哈尔滨","杭州","南昌","广州","福州"} ;
Map map = new LinkedHashMap();
for (int i=0;i<proAy.length;i++){
map.put(proAy[i],cityAy[i]);
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
|
例3:
Hashtable
对比:

2. Iterator
基本使用


例4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class Ex04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Stu> stuList = new ArrayList();
stuList.add(new Stu(19)) ;
stuList.add(new Stu(39)) ;
stuList.add(new Stu(14)) ;
stuList.add(new Stu(16)) ;
stuList.add(new Stu(26)) ;
stuList.add(new Stu(12)) ;
Iterator<Stu> iterator = stuList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Stu stu = iterator.next();
if (stu.getAge()>18){
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(stuList);
}
}
|
参考java8 List 删除元素:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| List list = new ArrayList() ;
list.add(new Stu(1,"aaa",19)) ;
list.add(new Stu(2,"bbb",16)) ;
list.add(new Stu(3,"ccc",14)) ;
list.removeIf(ele->((Stu)ele).getAge()>18) ;
list.forEach(System.out::println);
|
3. 泛型
为什么

怎么用

4. Set
4.1 HashSet

例5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;
public class Ex05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int blueBall = random.nextInt(16)+1 ;
HashSet<Ball> ballSet = new LinkedHashSet<>() ;
ballSet.add(new Ball("蓝球",blueBall)) ;
while (ballSet.size() != 7) {
int redBall = random.nextInt(33)+1 ;
ballSet.add(new Ball("红球",redBall)) ;
}
System.out.println(ballSet);
}
}
class Ball{
private String color ;
private Integer num ;
public Ball(String color, Integer num) {
this.color = color;
this.num = num;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Integer getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(Integer num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Ball ball = (Ball) o;
return Objects.equals(color, ball.color) &&
Objects.equals(num, ball.num);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(color, num);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Ball{" +
"color='" + color + '\'' +
", num=" + num +
'}';
}
}
|
5. Map练习
5.1 Map练习
例6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| 一、利用Map,完成下面的功能:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1930, "乌拉圭");
map.put(1934, "意大利");
map.put(1938, "意大利");
map.put(1950, "乌拉圭");
map.put(1954, "西德");
map.put(1958, "巴西");
map.put(1962, "巴西");
map.put(1966, "英格兰");
map.put(1970, "巴西");
map.put(1974, "西德");
map.put(1978, "阿根廷");
map.put(1982, "意大利");
map.put(1986, "阿根廷");
map.put(1990, "西德");
map.put(1994, "巴西");
map.put(1998, "法国");
map.put(2002, "巴西");
map.put(2006, "意大利");
map.put(2010, "西班牙");
map.put(2014, "德国");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入年份:");
int year = scanner.nextInt();
String msg = map.getOrDefault(year, "没有举办世界杯");
System.out.println(msg);
scanner.close();
}
}
|
例7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1930, "乌拉圭");
map.put(1934, "意大利");
map.put(1938, "意大利");
map.put(1950, "乌拉圭");
map.put(1954, "西德");
map.put(1958, "巴西");
map.put(1962, "巴西");
map.put(1966, "英格兰");
map.put(1970, "巴西");
map.put(1974, "西德");
map.put(1978, "阿根廷");
map.put(1982, "意大利");
map.put(1986, "阿根廷");
map.put(1990, "西德");
map.put(1994, "巴西");
map.put(1998, "法国");
map.put(2002, "巴西");
map.put(2006, "意大利");
map.put(2010, "西班牙");
map.put(2014, "德国");
Map<String, StringBuilder> teamMap = new HashMap<>() ;
map.forEach((year,name)->{
if (teamMap.containsKey(name)) {
StringBuilder sb = teamMap.get(name);
sb.append(year).append("\t") ;
}else {
teamMap.put(name, new StringBuilder(year + "\t"));
}
});
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一支球队的名字:");
String year = scanner.next();
String msg = teamMap.getOrDefault(year, new StringBuilder("没有获得过世界杯")).toString();
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
String inputTeamName = scanner.next();
AtomicBoolean isPrint = new AtomicBoolean(true);
map.forEach((year,name)->{
if (name.equals(inputTeamName)){
System.out.println(year);
isPrint.set(false);
}
});
if (isPrint.get()) {
System.out.println("没有获得过世界杯");
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
String inputTeamName = scanner.next();
List<Integer> yearList = new ArrayList<>() ;
map.forEach((year,name)->{
if (name.equals(inputTeamName)){
yearList.add(year) ;
}
});
if (yearList.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("没有获得过世界杯");
}
yearList.forEach(System.out::println);
|
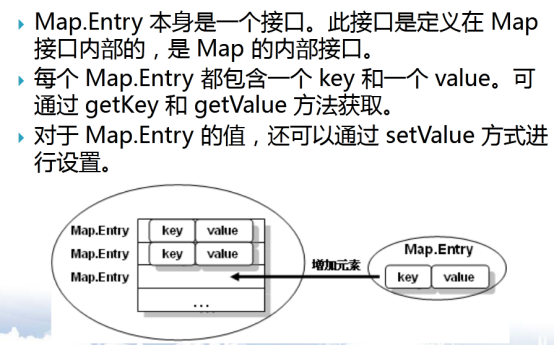
5.2 Map.Entry
5.3 Map综合案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class EX {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] nameAy = {"朱辛庄","育知路","平西府","回龙观东大街","霍营","育新","西小口","永泰庄","林萃桥","森林公园南门","奥林匹克公园","奥体中心","北土城"} ;
Map<Integer,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(nameAy.length) ;
for (int i = 0; i < nameAy.length; i++) {
map.put(i+1,nameAy[i]) ;
}
map.forEach((idx,name)-> System.out.println("第"+idx+"站:"+name));
}
}
|
例8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Ex08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] nameAy = {"朱辛庄","育知路","平西府","回龙观东大街","霍营","育新","西小口","永泰庄","林萃桥","森林公园南门","奥林匹克公园","奥体中心","北土城"} ;
Map<Integer,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(nameAy.length) ;
for (int i = 0; i < nameAy.length; i++) {
map.put(i+1,nameAy[i]) ;
}
map.forEach((idx,name)-> System.out.println("第"+idx+"站:"+name));
int money = caclMoney(13) ;
System.out.println("共:" + money);
}
private static int caclMoney(int count){
Map<Integer,Integer> moneyMap = new HashMap<>() ;
moneyMap.put(0,3) ;
moneyMap.put(1,3) ;
moneyMap.put(2,3) ;
moneyMap.put(3,3) ;
moneyMap.put(4,4) ;
moneyMap.put(5,4) ;
moneyMap.put(0,3) ;
moneyMap.put(0,3) ;
return count ;
}
}
|
例9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Num> numList = new ArrayList();
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put(1,"朱辛庄");
map.put(2,"育知路");
map.put(3,"平西府");
map.put(4,"回龙观东大街");
map.put(5,"霍营");
map.put(6,"育新");
map.put(7,"西小口");
map.put(8,"永泰庄");
map.put(9,"林萃桥");
map.put(10,"森林公园南门");
map.put(11,"奥林匹克公园");
map.put(12,"奥体中心");
map.put(13,"北土城");
for (Object j : map.keySet()){
System.out.println("第" +j +"站: " +map.get(j));
}
int i=1;
numList.add(new Num(1,3)) ;
numList.add(new Num(2,3)) ;
numList.add(new Num(3,3)) ;
numList.add(new Num(4,4)) ;
numList.add(new Num(5,4)) ;
numList.add(new Num(5+i,4+2*i)) ;
}
}
class Num{
int number ;
int money;
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public Num(int number,int money) {
this.number = number;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "homework.Num{" +
"number=" + number +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
|
例10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Ex09 {
private static String[] nameAy = {"朱辛庄","育知路","平西府","回龙观东大街","霍营","育新","西小口","永泰庄","林萃桥","森林公园南门","奥林匹克公园","奥体中心","北土城"} ;
private static Map<Integer,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(nameAy.length) ;
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < nameAy.length; i++) {
map.put(i+1,nameAy[i]) ;
}
map.forEach((idx,name)-> System.out.println("第"+idx+"站:"+name));
String beginName = "林萃桥" ;
String endName = "平西府";
int count = caclCount(beginName, endName);
int time = count*2 ;
int money = caclMoney(count) ;
System.out.println("从"+beginName+"到"+endName+"共经过"+count+"站收费"+money+"元,大约需要 "+time+"分钟");
}
private static int caclCount(String beginName,String endName){
Map<String,Integer> name2IndxMap = new HashMap<>() ;
map.forEach((idx,name)-> name2IndxMap.put(name,idx));
Integer beginIdx = name2IndxMap.get(beginName);
Integer endIdx = name2IndxMap.get(endName);
return Math.abs(beginIdx-endIdx) ;
}
private static int caclMoney(int count){
if (count<=3){
return 3 ;
}
if (count<=5){
return 4 ;
}
int money = 4+(count-5)*2 ;
if (money>10){
return 10 ;
}
return money ;
}
}
|
6.Set扩展
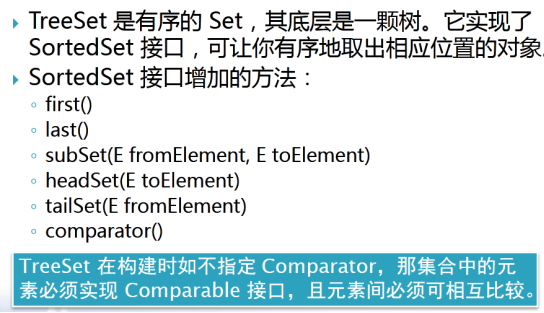
6.1 TreeSet
6.2 例11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package set;
import java.util.*;
public class Ex11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Customer> set = new TreeSet<>() ;
set.add(new Customer("小丽",500D)) ;
set.add(new Customer("小红",400.8)) ;
set.add(new Customer("小夏",400.3)) ;
set.add(new Customer("小花",700D)) ;
set.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
|
java8 外部排序写法:
1
| Set<Stu> set = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparingInt(Stu::getAge)) ;
|
7. Collections
7.1 辅助类

7.2 例12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package collections;
import set.Customer;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Ex12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Customer> customerList = Arrays.asList(new Customer("aaa",100D),new Customer("bbb",80.5D),new Customer("ccc",90D)) ;
Collections.sort(customerList,(c1,c2)->c1.getScore().compareTo(c2.getScore()));
customerList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
|
8. Map扩展
8.1 LinkedHashSet

8.2 LinkedHashMap

8.3 ConcurrentHashMap

8.4 Properties

9.泛型扩展
9.1 什么是泛型

9.2 泛型好处

9.3 使用前后对比


9.4 类型参数


9.5 方法参数




9.6 泛型不是协变的

9.7 类型通配符


9.8 泛型局限性






































